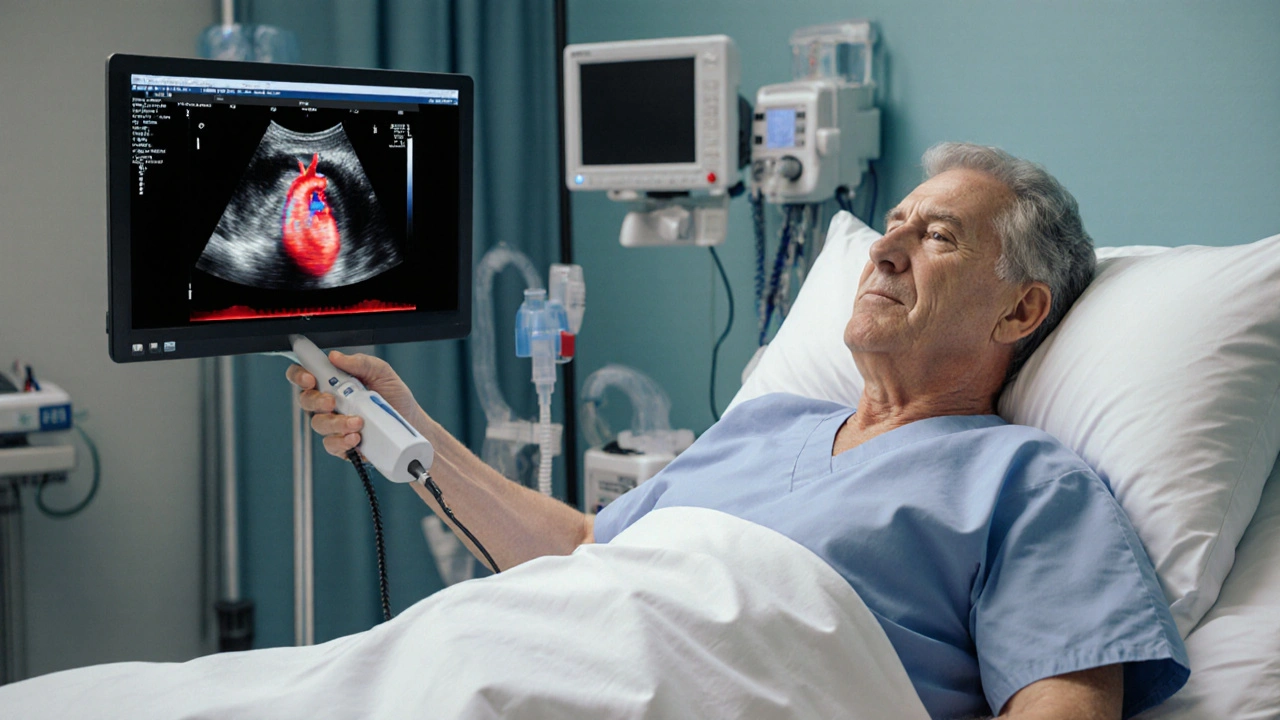
Echocardiography: Essential Cardiac Imaging
When working with Echocardiography, a non‑invasive ultrasound method that creates real‑time images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood flow. Also known as cardiac echo, it helps clinicians spot problems without surgery. Doppler ultrasound, a technique that measures the speed and direction of blood flow and Cardiac stress testing, an exercise‑ or drug‑induced assessment of heart performance are often combined to give a full picture of cardiac health.
Why Echocardiography Matters
echocardiography isn’t just a picture‑taking tool; it’s a diagnostic engine. It encompasses two‑dimensional (2‑D) imaging of the left and right ventricles, allowing doctors to measure wall thickness, ejection fraction, and chamber size. Those numbers translate directly into treatment decisions, whether you’re adjusting heart‑failure meds or planning a valve replacement.
One of the core strengths of echocardiography is its ability to assess valve function. By visualizing leaflets opening and closing, clinicians can grade stenosis or regurgitation severity. This information often guides the choice of anticoagulants or diuretics, linking imaging findings to the medication guides you’ll see later in this collection.
Doppler component adds a flow‑focused layer. It captures velocities across the mitral valve, aortic outflow tract, and pulmonary arteries. From those velocities, pressure gradients are derived, helping to pinpoint pulmonary hypertension or aortic stenosis. The data feed directly into risk scores that determine whether a patient needs a beta‑blocker, an ACE inhibitor, or more advanced therapy.
When you pair a resting echo with a stress echo, you get functional insight. Stress echo reveals how the heart reacts to increased demand, exposing ischemia that a static image might miss. This functional readout is critical for deciding on anti‑anginal drugs, statins, or even revascularization procedures.
The technology itself has evolved. Portable hand‑held probes now deliver bedside imaging in emergency rooms, while high‑end machines offer 3‑D reconstruction and strain imaging for detailed myocardial analysis. Knowing which device fits your setting can affect workflow and ultimately patient outcomes.
Interpreting an echo report isn’t just about numbers; it’s about context. A clinician must weigh imaging results against a patient’s medication list, comorbidities, and lifestyle. That’s why our article collection includes practical guides on buying generic drugs safely—because the right medication, paired with accurate imaging, is the cornerstone of effective care.
Below you’ll find a curated set of posts that blend cardiac imaging fundamentals with real‑world advice on medication safety, dosage considerations, and cost‑effective purchasing. Dive in to see how high‑quality echo data and smart drug choices work together to keep hearts healthy.
How Echocardiography Guides Embolism Diagnosis and Management
Explore how bedside echocardiography detects clot sources, assesses right‑heart strain, and guides treatment decisions for embolism, with practical tips, comparisons, and FAQs.